What Is Collagen?
In nature, collagen is a protein found exclusively in animals, particularly in the skin, bones, and connective tissues of mammals, birds, and fish. In fact, collagen is actually a family of proteins, and together they represent about a third of the total protein content in mammals.
The term collagen is derived from the Greek word κόλλα (Kólla), meaning "glue," combined with the suffix “-gen,” which means "producing."
What Does Collagen Do?
Simply put, collagen helps maintain the structural integrity of tissues and organs throughout the body. Different types of collagen are found in various tissues, yet they all share the common feature of having three polypeptide chains coiled together in a triple helix structure. For the health and well-being of pets, types I, II, and III are of most interest:
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen, making up more than 90% of the protein content of bone and is the major collagen of tendons (this type of connective tissue attaches muscles to bones) and ligaments (this type of connective tissue attaches one bone to another bone – holding joints together), providing structure and strength to these tissues.
Type I and III collagen is abundant in the dermis layer of the skin providing structural support as well as elasticity to maintain the firmness and suppleness of this organ – a very important barrier to keep moisture in and invading organisms and toxins out of the body.
Type II collagen is the predominant component of cartilage, the extremely strong, flexible and semi-rigid support tissue found at points where two bones meet, providing a smooth surface that allows joints to move easily and a ‘cushion’ effect to absorb the shock of impact, especially on the ends of weight-bearing bones (e.g. hip, elbow joints).
Collagen is also present in all the smooth muscle tissues, blood vessels, digestive tract, heart, gallbladder, kidneys and bladder, holding the cells and tissues together.
Skin & Coat Health
Types I and III collagen are crucial for maintaining strong, healthy skin and coat.
They help preserve skin elasticity and hydration.
They may also help relieve dry, itchy skin.
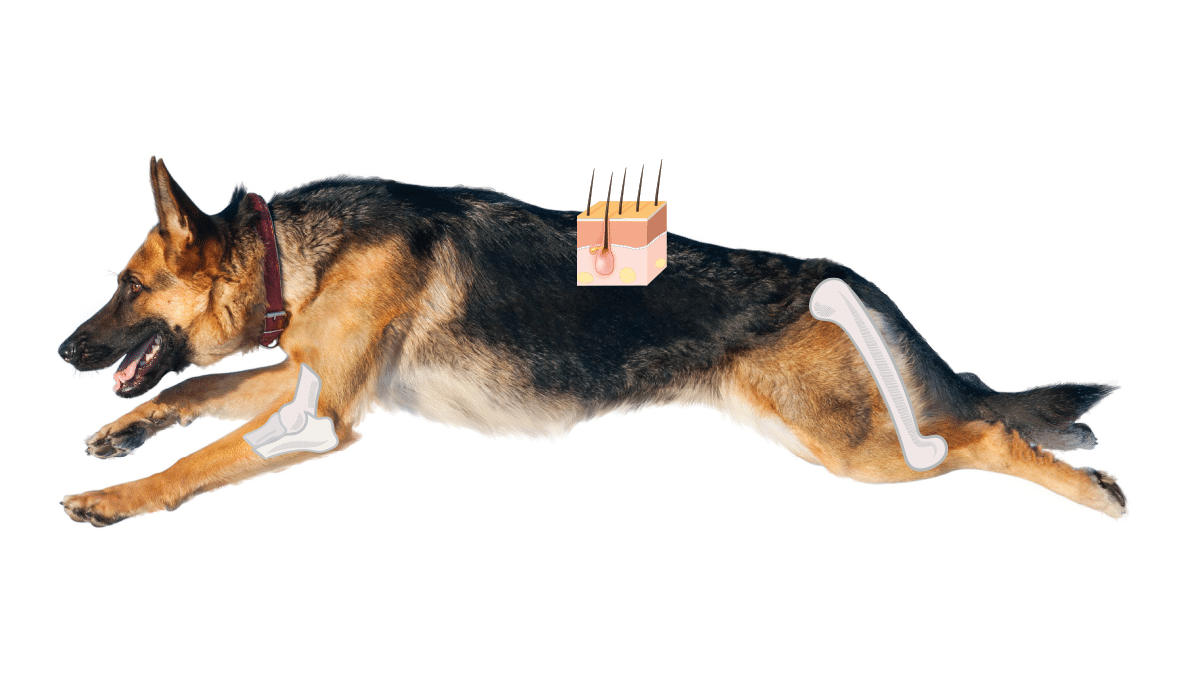
Joint Health
• Types I and II collagen are essential components of cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
• They support robust joint health in young, active dogs.
• They help maintain mobility and flexibility in older dogs.
Bone Health
• Type I collagen makes up 90% of the protein content in bone.
• It provides the framework for bone mineralisation.
• It is vital for strong, healthy bones across all life stages.
How Is Collagen Made?
Like all proteins, collagen is built from amino acids. However, collagen’s distinctive amino acid composition includes high levels of glycine (Gly) and proline (Pro), along with hydroxyproline (Hyp), a derivative of proline. These amino acids are arranged in a repeating pattern, often following the sequence Gly-Pro-X or Gly-X-Hyp (where X can be any amino acid).
All collagen types consist of three polypeptide chains that form a triple helix. Depending on the type, these chains may be identical or composed of two or more different chains.
Over time, collagen undergoes natural cycles of breakdown and regeneration. Daily wear and tear—as well as the ageing process—can accelerate its degradation. As pets age, collagen production slows, resulting in thinner, more fragile skin, reduced elasticity in tendons and ligaments, and stiffer, potentially painful joints.
Dietary Collagen & Collagen Peptides
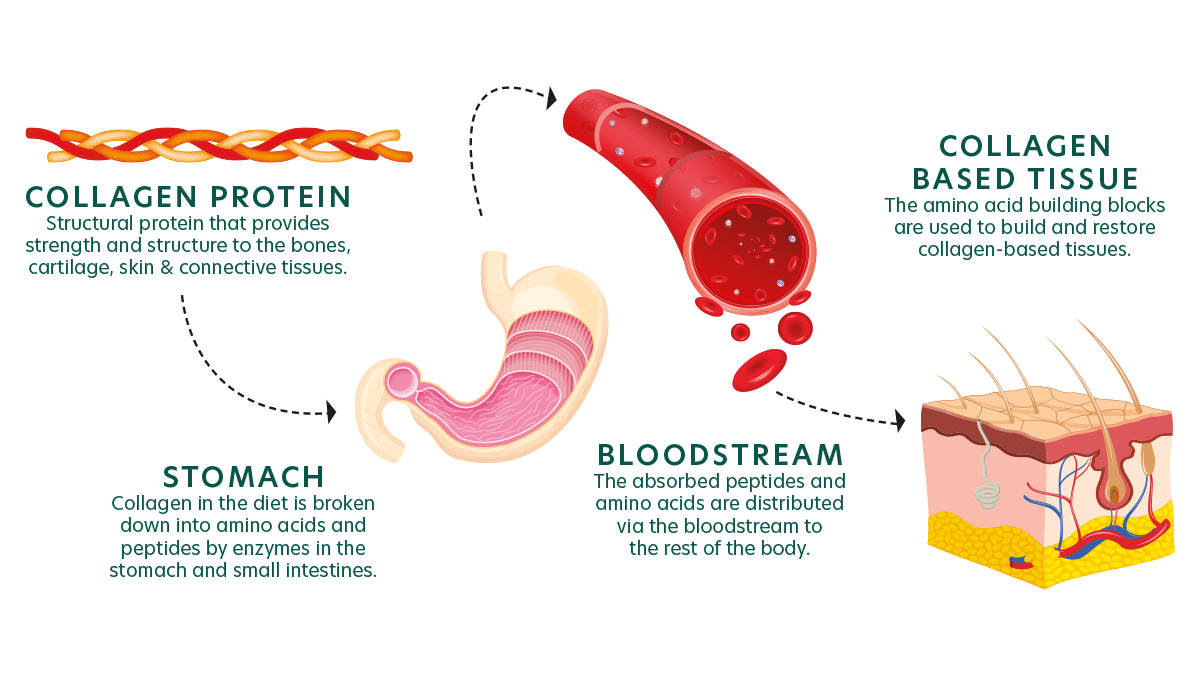
At GA Pet Food Partners, we take pride in sourcing the finest meat and fish ingredients directly from trusted suppliers.. These ingredients naturally contain collagen, though the amounts can vary across different animal tissues. For example, when testing various parts of a whole chicken, the highest collagen content is found in the skin, followed by the carcass (bones and cartilage), with lower amounts present in skeletal meat and internal organs.
Kibbles prepared with naturally collagen-rich ingredients, such as freshly prepared meat and fish materials, are digested and absorbed by pets. This process provides the essential building blocks, particularly the amino acids glycine and proline, that support the body in producing more collagen, thereby helping to maintain healthy bones, joints, and skin.
The GA Difference
Research has shown that collagen peptides are more readily absorbed by the digestive tract than intact proteins. To maximise the potential benefits of dietary collagen, optimal absorption is key.
Thanks to our latest R&D work on protein hydrolysis and our innovative ‘Highly Digestible Protein (HDP) process, GA Pet Food Partners is able to “pre-digest” the collagen in our selected meat and fish ingredients. Through carefully controlled enzymatic hydrolysis, the collagen is broken down into peptides before being incorporated into our delicious kibble.
Potential Benefits of Dietary Collagen and Collagen Peptides
While research in dogs and cats remains limited, studies in other animals and humans suggest that dietary collagen and collagen peptides may offer several health benefits for pets:
Bone Health
Collagen is essential for bone health, providing the protein matrix that supports bone mineralisation.
Bone collagen is in a constant state of breakdown and renewal, so supplementing with dietary collagen or collagen peptides can help maintain strong, healthy bones throughout life.
Skin and Coat Health
The dermis of a dog’s skin is predominantly composed of collagen. Ensuring a good supply of collagen in the diet can help maintain skin elasticity and support overall skin and fur health.
Joint Health
Healthy joints require robust cartilage, ligaments, and tendons—all of which contain high levels of collagen.
Supporting collagen levels in the diet is crucial not only for young, active dogs but also for preventing age-related joint pain and mobility issues.
By incorporating collagen-rich ingredients and utilising advanced processing techniques, GA Pet Food Partners aims to deliver pet food that supports your pet’s overall health and well-being.

Dr Adrian Hewson-Hughes
Nutrition, Food Safety and Innovation Advisor
Adrian graduated from the University of Sunderland with a BSc (Hons) in pharmacology and went on to work in a Multiple Sclerosis laboratory at the Institute of Neurology, University College London where he obtained a PhD. After several more years as a ‘postdoc’ in academia at the Universities of Cambridge and Nottingham, he joined Mars Petcare and spent 14 years working in R&D at the Waltham Centre for Pet Nutrition. Adrian led various research projects on palatability, feeding behaviour, nutrition and metabolism in both cats and dogs resulting in scientific publications, presentations and product innovations. In October 2018, Adrian joined GA, excited by the opportunity to support the continued innovation and investment that GA commits to, bringing the highest quality products to our Partners and our pets.
You may also like...
Article written by Dr Adrian Hewson-Hughes
The Pros and Cons of AI in Pet Retail
You may have frequently encountered the term “AI” or “AI technology” in the media. From unlocking your phone using Face ID, asking for directions on your [...]




